Battery with a certain capacity, does not allow the use on an ongoing basis to supply the electricity needs of the engine or other components on the car.
Therefore, the car needed a system that can charge the battery as well as a power source that supplies power directly to components that are needed when the machine is turned on. This system is called a charging system.
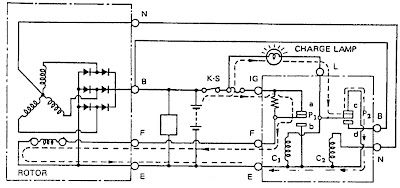
The main components comprising a battery charging system, alternator, ignition and regulator, as shown in the figure below:
1. Alternator
Alternator function is to supply an electric current when the engine life. But if the amount of electricity generated is greater than the alternator, the battery Come with the electrical burden.
Part of the alternator
a. pulleys
Pulleys serves to receive mechanical power from the engine to rotate the rotor
b. Fan
The fan cools the diode circuit and the coil in the alternator coil.
c. Rotor
In the alternator, the rotor is moving (rotating). Rotor serves to generate a magnetic field. The nails on the rotor serves as the magnetic poles and two slip ring functioning as intermediaries for distributing power to the rotor coil. Note the picture below:
d. Stator
The stator consists of: Stator Coil and Stator Core
e. End frame
At the end frames are ventilation holes for cooling air place.
f. Rectifier
Rectifier diodes consist of 3 positive, 3 negative diodes and diode holder.
Diode holder serves to radiate heat and prevent heat diode
g. Regulator
The regulator controls the flow of electricity coming into the rotor coil, so that the voltage generated by the alternator fixed (constant) in accordance with predetermined prices, although the engine that drives the rotation changes. In addition, the regulator also serves on the battery charging when the battery is full and the alternator is able to supply their own electrical current to the part that requires an electric current.